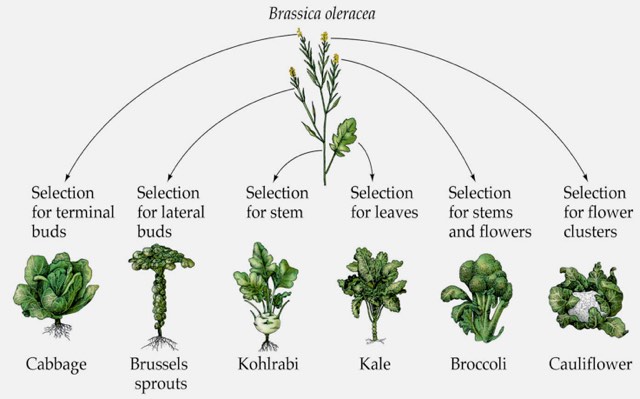
The greatest variation was shown through the ratios. The greatest variation was shown through how much bigger or smaller a plant was compared to another in size. The greatest variation is shown when comparing the plants ratios in sizes. Plants, 2, and 4 are the biggest, and Plant 3 is the smallest. Plants 1 and 2 are the same. When comparing the biggest to the smallest, plant 2 has a height of 10.5 inches and plant 3 has a height of 4.5 inches, plant 2 is 6 inches taller then plant 3, and when comparing their widths, plant 2 has a width of 4.5 and plant 3 has a width of 2, with a 2.5 inch difference.
Ratio Table
Plant 1 (Collards): 6:5
Plant 2 (Kohlrabi light color): 10.5:4.5
Plant 3 (Kale): 4.5:2
Plant 4 (Kohlrabi dark color): 9.5:5.5
Plant 5 (Sabboy Cabbage): 6:5
2. There is a lot of variability in the domestic forms of Brassica oleracea because they are all different plants. Each plant has its own traits, which is a distinguishing quality or characteristic about the plant that is different from each other. For example, from question 1, Plant 2 has bigger leaves, and plant 3 has smaller leaves. Also there are selective breeding and artificial selection. They are both very similar, and contribute to the variations of the Brassica oleracea plants, except there is a slight difference between the two. Selective breeding is done by humans, where they basically select the traits they want on the plant, and plant it in, but artificial breeding is done by nature and is not controlled. The genes of each plant vary, and also can be due to the selective breeding because each plant was chosen to be planted, and each has a specific purpose. Descent with modification also has an affect on the variability. Its when a trait is passed from parent to offspring. In this case traits from the past forms of the plant went through different mutations to be where they are now in their current state inside the garden. This also has relation to natural variation because it refers to genetic diversity of a plant species, each plant is diverse in its own way, and went through descent with modification and mutations to be where its at now.
3. The part that seemed to be all consistently the same with each Brassica oleracea plant was the color of the leaves. Every single one of the plants had a shade of green leaf. I think they are all similar/ the same in color because each one has green chloroplasts inside of the leaves. When light beams on each leaf,it reflects green light that our eyes see because of the chlorophyll found in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplast. The images I will show below will show the color of each leaf.

 4. To get the leaves to not be green, a plant breeder would have to mutate the plant. The breeder would need to have the plant in an area where it could absorb no light, but even then this would not work, a plant needs photons from a light source to survive, without them, the plant would die. So in this case, its pretty difficult. Some people color water with dye, and use it to water flowers to make them different colors because the flower is absorbing the dyed water, so the breeder could attempt something like that. They could also try to grow the plant with a different source of light that is not the sun, and see if the plants color will vary at all in its green shade. Other then that, changing a plants color, and especially Brassica oleracea plants is difficult, but those options may work.
4. To get the leaves to not be green, a plant breeder would have to mutate the plant. The breeder would need to have the plant in an area where it could absorb no light, but even then this would not work, a plant needs photons from a light source to survive, without them, the plant would die. So in this case, its pretty difficult. Some people color water with dye, and use it to water flowers to make them different colors because the flower is absorbing the dyed water, so the breeder could attempt something like that. They could also try to grow the plant with a different source of light that is not the sun, and see if the plants color will vary at all in its green shade. Other then that, changing a plants color, and especially Brassica oleracea plants is difficult, but those options may work.